The Rich Tapestry of Morocco’s History
Nestled at the crossroads of Africa, Europe, and the Middle East, Morocco boasts a history as diverse and vibrant as its landscapes. From ancient Berber tribes to Arab conquerors and European colonisers, the story of Morocco weaves together a tapestry of cultural influences that have shaped this North African nation into the captivating destination it is today.
Ancient Roots
The history of Morocco dates back thousands of years to the time of the indigenous Berber people. These early inhabitants left their mark on the land through intricate cave paintings, megalithic tombs, and fortified cities such as Volubilis. The Phoenicians, Carthaginians, and Romans all established settlements along Morocco’s coast, contributing to its rich archaeological heritage.
Arab Conquest
In the 7th century AD, Arab armies swept across North Africa, introducing Islam to the region and establishing dynasties that would rule over Morocco for centuries. The Umayyad Caliphate, followed by the Almoravid and Almohad empires, brought architectural marvels like the Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakech and religious scholarship that still influences Moroccan society today.
Colonial Era
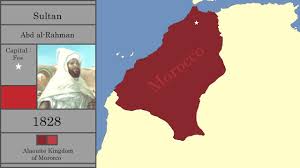
In the 19th and 20th centuries, European powers vied for control over Morocco. The country became a protectorate divided between France and Spain in 1912. This period of colonial rule left lasting legacies on Moroccan culture, language, and governance structures. Independence was finally achieved in 1956 after years of struggle against foreign domination.
Modern Morocco
Since gaining independence, Morocco has undergone significant social and economic development under the rule of King Mohammed VI. The country has embraced tourism as a key industry, attracting visitors with its bustling souks, majestic palaces, and stunning natural beauty. Efforts to preserve traditional crafts and promote sustainable tourism have helped showcase Morocco’s unique identity to the world.
Cultural Heritage
Today, Morocco stands as a melting pot of traditions where ancient customs blend seamlessly with modern influences. The vibrant music scene, colourful festivals like Eid al-Adha and Mawazine Festival Rhythms of the World, and delectable cuisine all reflect the diverse heritage that defines Moroccan identity.
As you traverse through the bustling medinas or gaze upon the Atlas Mountains at sunset, remember that each stone laid in Morocco tells a story—a story of resilience, creativity, and enduring beauty that continues to captivate travellers from around the globe.
Unveiling the Tapestry of Time: Nine Key Insights into Morocco’s Historical Saga
- Morocco has a rich history dating back to ancient times, with influences from Berber, Arab, and European cultures.
- The country was once part of the Roman Empire and later came under Islamic rule in the 7th century.
- Morocco was a major centre for trade and commerce due to its strategic location along the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean.
- The Almoravid and Almohad dynasties were significant in shaping Morocco’s history during the medieval period.
- Morocco was colonised by France and Spain in the 20th century before gaining independence in 1956.
- The country has a diverse architectural heritage, with examples of Islamic, Moorish, and French colonial styles.
- Moroccan cuisine is influenced by its history, combining Berber, Arab, Andalusian, and Mediterranean flavours.
- Traditional Moroccan music such as Gnawa and Andalusian music reflects the country’s diverse cultural influences over time.
- ‘The Battle of Three Kings’ in 1578 was a significant event in Moroccan history when Portuguese forces were defeated by Moroccan Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur.
Morocco has a rich history dating back to ancient times, with influences from Berber, Arab, and European cultures.
Morocco’s captivating history is a tapestry woven with threads of ancient civilisations, where the echoes of Berber tribes, Arab conquerors, and European colonisers resonate through the ages. From the rugged Atlas Mountains to the sun-kissed shores of its coastal cities, Morocco’s diverse landscapes bear witness to the rich tapestry of cultural influences that have shaped this North African nation.
The country was once part of the Roman Empire and later came under Islamic rule in the 7th century.
Once a part of the illustrious Roman Empire, Morocco’s history took a significant turn in the 7th century when it fell under Islamic rule. This transition marked a pivotal moment in shaping the cultural and religious landscape of the region, as Islam became deeply ingrained in the fabric of Moroccan society. The echoes of these historical events can still be felt today, adding layers of complexity and richness to Morocco’s captivating heritage.
Morocco was a major centre for trade and commerce due to its strategic location along the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean.
Morocco’s pivotal role in history as a major centre for trade and commerce can be attributed to its strategic location along the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean. Situated at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, Morocco served as a vital hub for merchants and traders seeking to exchange goods, ideas, and cultures. The bustling ports of Morocco facilitated the flow of spices, textiles, and precious metals, enriching the country’s economy and fostering a dynamic cultural exchange that continues to shape Morocco’s identity today.
The Almoravid and Almohad dynasties were significant in shaping Morocco’s history during the medieval period.
The Almoravid and Almohad dynasties played a crucial role in shaping Morocco’s history during the medieval period. Emerging as powerful Islamic empires in the 11th and 12th centuries, these dynasties left a lasting impact on the region through their military conquests, architectural achievements, and promotion of Islamic scholarship. Under their rule, Morocco witnessed a flourishing of art, culture, and commerce, setting the stage for the country’s future development and influencing its identity to this day.
Morocco was colonised by France and Spain in the 20th century before gaining independence in 1956.
In the 20th century, Morocco found itself under the colonial rule of France and Spain, marking a tumultuous period in its history. The influence of these European powers shaped the socio-political landscape of the country, leaving a lasting impact on its culture and governance. However, after years of struggle and resistance against foreign domination, Morocco finally reclaimed its independence in 1956. This pivotal moment marked a new chapter in the nation’s history, as it embarked on a journey towards self-determination and sovereignty.
The country has a diverse architectural heritage, with examples of Islamic, Moorish, and French colonial styles.
Morocco’s architectural heritage is a testament to its rich history and cultural influences. The country showcases a diverse array of architectural styles, ranging from the intricate Islamic designs of mosques and madrasas to the ornate Moorish palaces with their stunning tile work and intricate carvings. Additionally, remnants of the French colonial era can be seen in the grand boulevards and elegant buildings scattered throughout cities like Casablanca and Rabat. This blend of Islamic, Moorish, and French colonial architecture creates a visual tapestry that reflects Morocco’s multifaceted past and present.
Moroccan cuisine is influenced by its history, combining Berber, Arab, Andalusian, and Mediterranean flavours.
Moroccan cuisine is a delightful reflection of the country’s rich history, blending a tapestry of culinary influences from Berber, Arab, Andalusian, and Mediterranean traditions. The diverse flavours and ingredients used in Moroccan dishes showcase the cultural melting pot that defines the nation, creating a unique gastronomic experience that tantalises the taste buds with every bite. From aromatic tagines to fluffy couscous and sweet pastries, each dish tells a story of Morocco’s past and present, inviting diners to savour a delicious journey through time.
Traditional Moroccan music such as Gnawa and Andalusian music reflects the country’s diverse cultural influences over time.
Traditional Moroccan music, including Gnawa and Andalusian melodies, serves as a captivating reflection of the country’s rich and varied cultural heritage that has evolved over centuries. The rhythmic beats of Gnawa music, with its roots in sub-Saharan Africa, blend seamlessly with the intricate melodies of Andalusian music brought by Muslim refugees from Spain. This fusion of diverse musical traditions not only entertains but also tells a compelling story of Morocco’s history and the interwoven tapestry of influences that have shaped its unique sound.
‘The Battle of Three Kings’ in 1578 was a significant event in Moroccan history when Portuguese forces were defeated by Moroccan Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur.
The Battle of Three Kings in 1578 stands as a pivotal moment in Moroccan history, marking the decisive victory of Moroccan Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur over the Portuguese forces. This historic event not only showcased the military prowess of the Moroccan army but also solidified Morocco’s position as a formidable power in the region. The defeat of the Portuguese at the hands of Sultan Ahmad al-Mansur reverberated across Europe and North Africa, leaving a lasting impact on the political landscape of the time and shaping the course of Moroccan history for years to come.